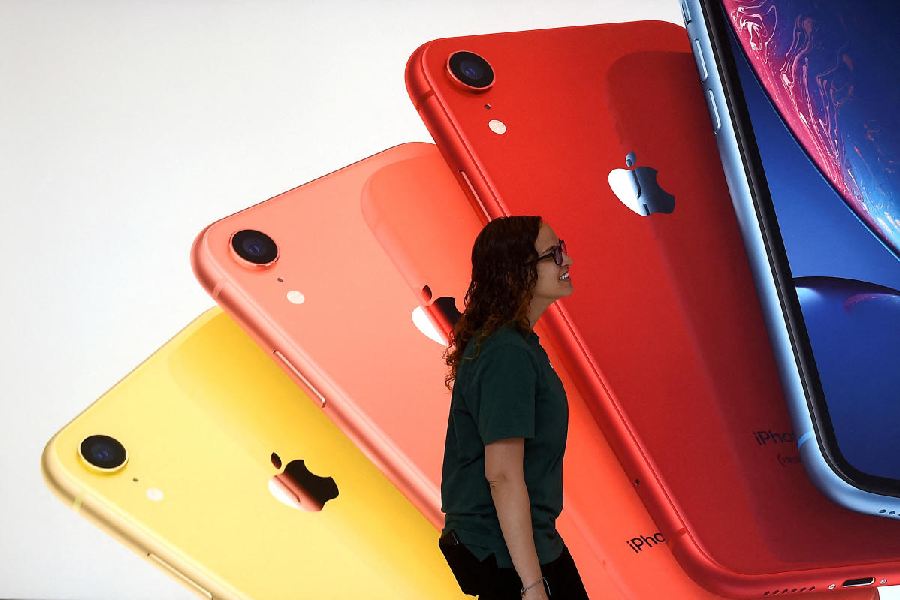
Apple’s decision to expand production of its upcoming iPhone 17 series in India marks a pivotal moment in the company’s global manufacturing strategy. For the first time, all four models of the iPhone 17 lineup—including the iPhone 17, iPhone 17 Pro, iPhone 17 Pro Max, and the newly introduced iPhone 17 Air—are being assembled in India ahead of their September 2025 launch. This move not only signals Apple’s intent to reduce its reliance on China but also underscores India’s growing importance as a global manufacturing hub.
Let’s explore the implications of this shift, the operational dynamics behind it, and what it means for Apple, India, and the broader tech industry.
A Historic Manufacturing Milestone
Apple began assembling iPhones in India in 2017, initially focusing on older models like the iPhone SE. Over the years, the company gradually increased its footprint, producing newer models and expanding its partnerships with local manufacturers. However, the iPhone 17 series marks the first time Apple is manufacturing an entire flagship lineup in India from the outset.
This expansion spans five major facilities across the country, including newly operational plants run by Tata Group in Hosur, Tamil Nadu, and Foxconn near Bengaluru. These factories are now producing not just the standard models but also the premium Pro variants, which were previously exclusive to Chinese assembly lines.
Strategic Drivers Behind the Shift
Several factors have influenced Apple’s decision to scale up production in India:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing trade disputes and tariff uncertainties between the U.S. and China have prompted Apple to diversify its supply chain. By shifting production to India, Apple can mitigate risks associated with potential export restrictions or increased costs.
- Government Incentives: India’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme has made local manufacturing more attractive. Apple’s partners benefit from financial incentives tied to output and export performance, encouraging deeper investment in Indian operations.
- Labor and Infrastructure: India offers a large, skilled workforce and improving infrastructure, particularly in tech-centric regions like Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. These conditions support high-volume, high-quality manufacturing.
- Market Potential: India is not just a manufacturing base—it’s also a rapidly growing consumer market. Local production helps Apple price its devices more competitively, avoiding import duties and appealing to a broader segment of Indian buyers.
Tata and Foxconn: The Pillars of Expansion
Apple’s manufacturing push in India is anchored by two key partners: Tata Group and Foxconn.
- Tata Group: The Indian conglomerate has emerged as a critical player in Apple’s supply chain. Its Hosur facility is expected to handle nearly half of all iPhone production in India over the next two years. Tata’s growing role reflects Apple’s confidence in its capabilities and its commitment to building a robust local ecosystem.
- Foxconn: The Taiwanese electronics giant continues to be Apple’s largest contract manufacturer globally. In India, Foxconn operates multiple plants, including a major facility near Bengaluru airport and another in Chennai. These plants are now producing the iPhone 17 series for both domestic and international markets.
Together, Tata and Foxconn represent a powerful manufacturing alliance that enables Apple to scale rapidly while maintaining quality and efficiency.
Export Surge and Economic Impact
Apple’s expanded production in India is already yielding significant economic dividends. Between April and July 2025 alone, the company exported smartphones worth $7.5 billion from India. This figure is expected to rise sharply as the iPhone 17 series ramps up, with total exports projected to exceed $20 billion by the end of the fiscal year.
The increase in exports not only boosts India’s trade balance but also strengthens its reputation as a reliable manufacturing destination. It creates thousands of jobs, stimulates ancillary industries, and encourages further foreign investment in the country’s tech sector.
Navigating Tariff Challenges
Apple’s shift to India also helps the company navigate complex tariff landscapes. While the U.S. administration has imposed reciprocal tariffs on several countries, electronics—particularly smartphones—have so far been exempt. Nevertheless, uncertainty looms, and Apple’s proactive move to produce U.S.-bound iPhones in India positions it to weather potential policy changes.
Interestingly, Apple has reportedly replaced many Chinese engineers at its Indian facilities with personnel from Taiwan and Japan. This adjustment reflects both geopolitical sensitivities and Apple’s commitment to maintaining operational continuity despite external pressures.
The iPhone 17 Lineup: What’s Coming
The iPhone 17 series is expected to include four models:
- iPhone 17: The standard model, featuring incremental upgrades in performance and camera capabilities.
- iPhone 17 Pro: A premium variant with advanced display technology and enhanced processing power.
- iPhone 17 Pro Max: The flagship device, likely to include new camera sensors, improved battery life, and exclusive software features.
- iPhone 17 Air: A new addition to the lineup, potentially replacing the Plus model. It’s expected to offer a larger display in a lighter form factor, targeting users who want premium features without the bulk.
All models are being produced in India, and Apple is reportedly preparing to launch them globally on September 9, 2025.
Implications for the Global Tech Landscape
Apple’s manufacturing expansion in India sends ripples across the global tech industry:
- Supply Chain Diversification: Other tech giants may follow Apple’s lead, seeking to reduce dependence on China and explore alternative manufacturing bases.
- India’s Rise: The country’s role in global electronics manufacturing is being redefined. From a peripheral player, India is now emerging as a central hub for high-end consumer electronics.
- Innovation and Investment: Increased production often leads to greater investment in R&D, logistics, and infrastructure. India could see a surge in innovation ecosystems around these manufacturing centers.
Looking Ahead: Sustainability and Scalability
Apple’s long-term vision appears to include deeper integration with India’s manufacturing ecosystem. Reports suggest that Tata could eventually produce half of all iPhones made in India, and plans for iPhone 18 production in the country are already underway.
This trajectory aligns with Apple’s broader goals of sustainability, scalability, and resilience. By building a diversified supply chain that includes India as a cornerstone, Apple is better equipped to handle global disruptions while maintaining its commitment to quality and innovation.
Conclusion: A Strategic Realignment
The expansion of iPhone 17 series production in India is more than a logistical adjustment—it’s a strategic realignment of Apple’s global operations. It reflects the company’s response to geopolitical shifts, economic incentives, and evolving consumer dynamics.
For India, it’s a validation of its manufacturing capabilities and a gateway to deeper integration with the global tech economy. For Apple, it’s a bold step toward building a more resilient, diversified, and future-ready supply chain.
As the iPhone 17 series prepares to hit shelves worldwide, its Indian origins will stand as a testament to a new era in global manufacturing—one where innovation, strategy, and geography converge to shape the future of technology.